Topology Optimization for Hybrid Additive-Subtractive Manufacturing
This research focuses on topology optimization specifically tailored for hybrid additive-subtractive manufacturing (HASM). The objective is to design structures that are fully compatible with both additive and subtractive processes, ensuring manufacturability while improving surface quality.
1.Research Background
2.Design Framework
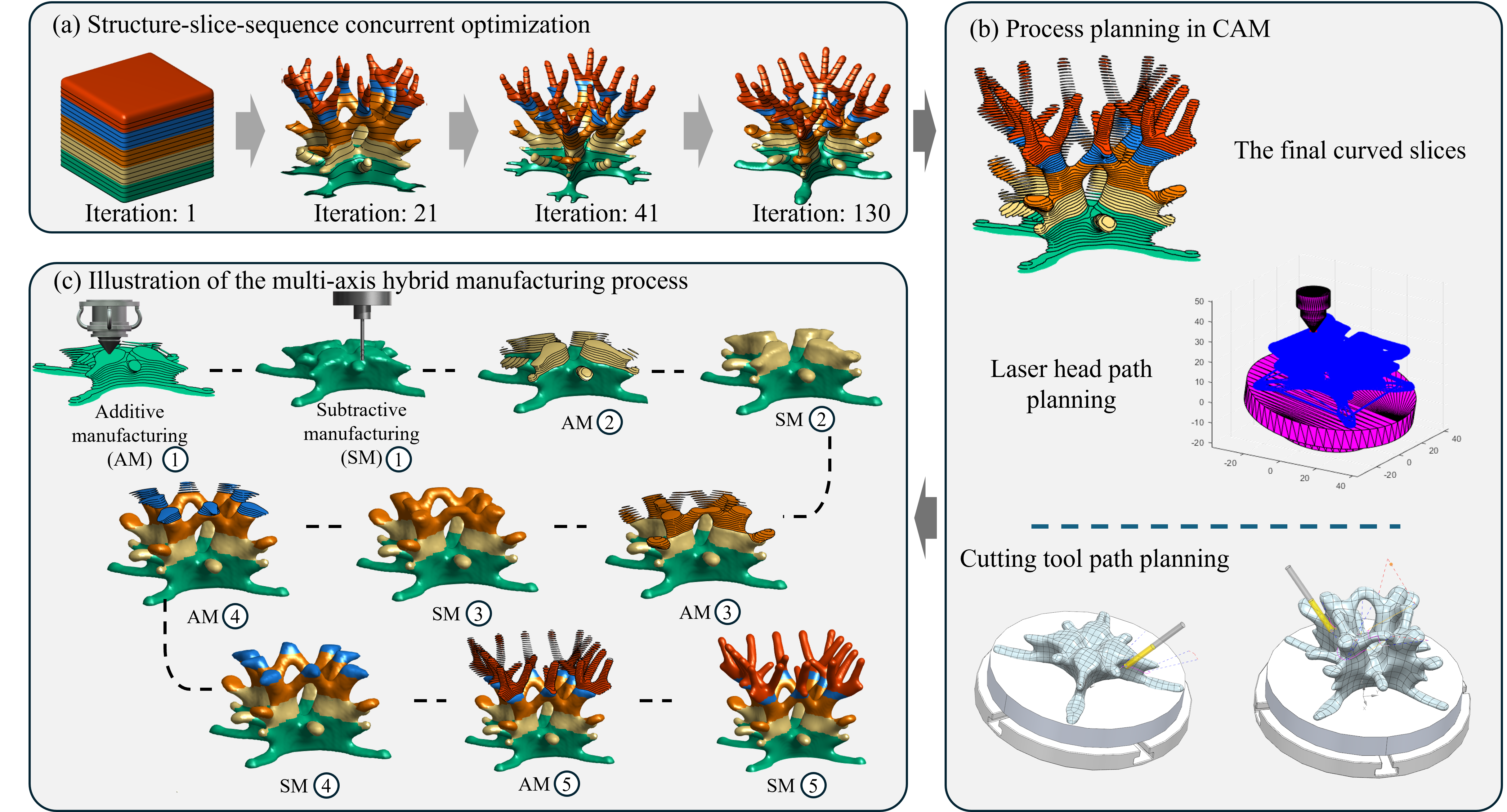
Design flow chart [2].
The structural design, additive manufacturing slicing, partitioning for hybrid additive-subtractive processes, and the number of partitions will be collaboratively optimized!
3.Fabrication Validation

Overall machining process for hybrid manufacturing.
The machining process consists of three stages. The majority of the solid part is processed during the first two stages, with 32.7% completed after the first stage and 81.5% after the second. To maximize workspace and avoid collisions, cutting tools for subtractive operations during additive phases are manually removed and reinstalled with minimal setup time.
3.1.Hybrid Fabrication Stages
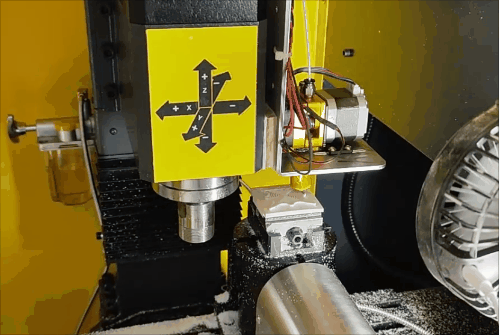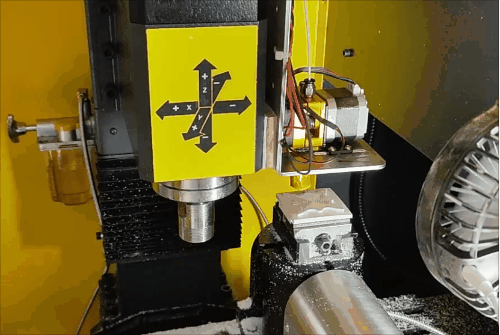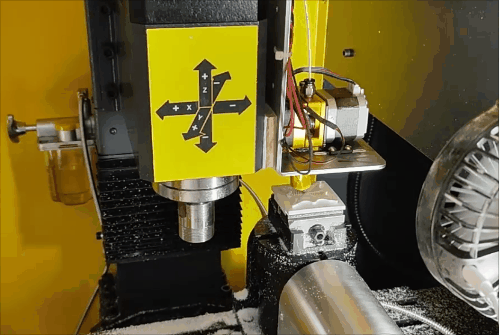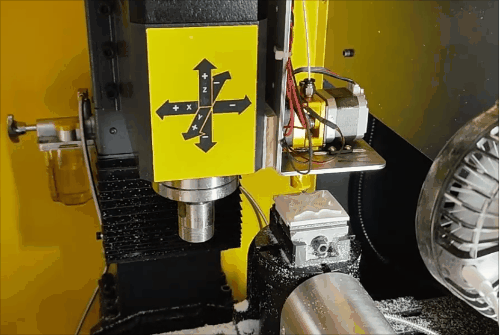
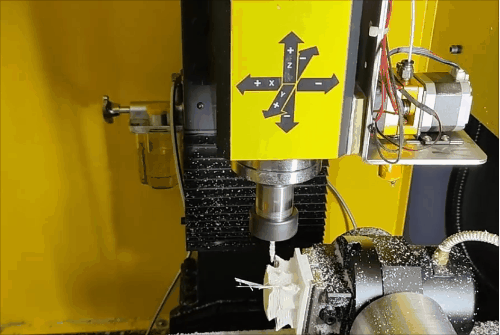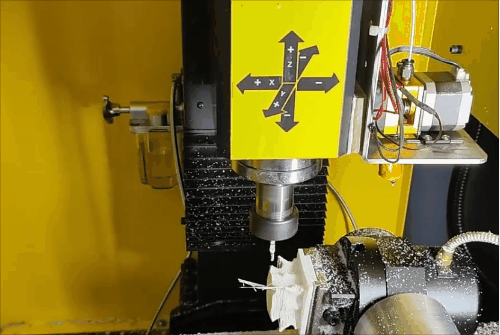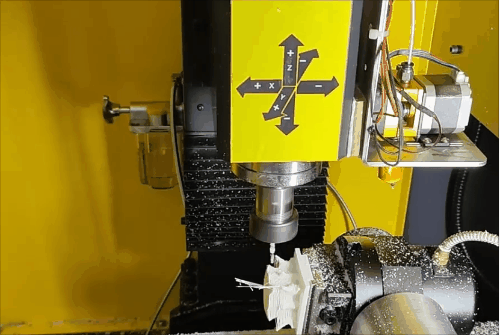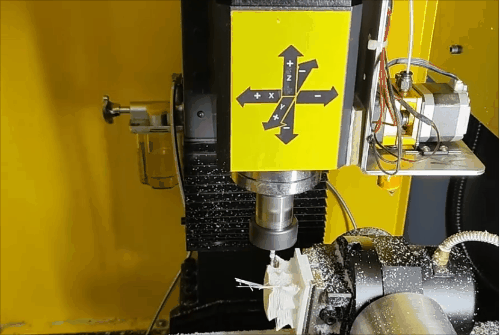
Stage 1 of hybrid fabrication.
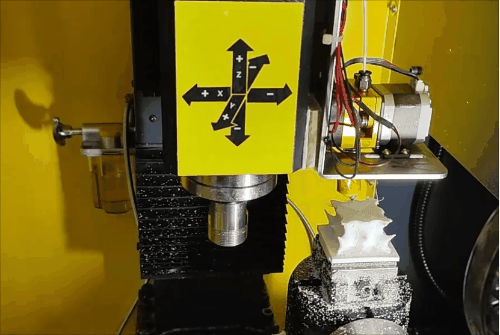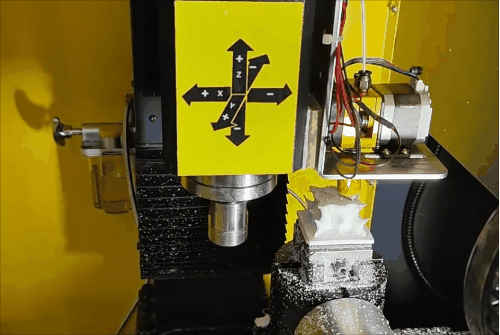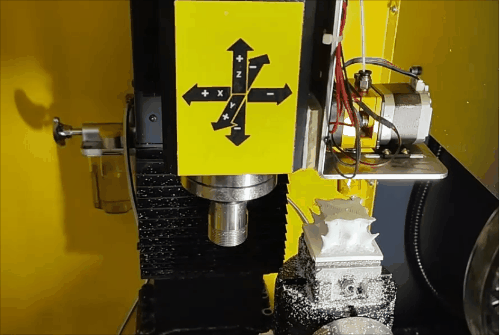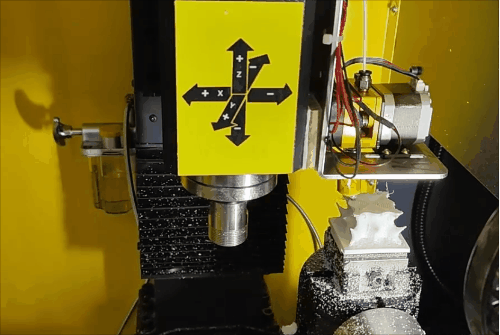
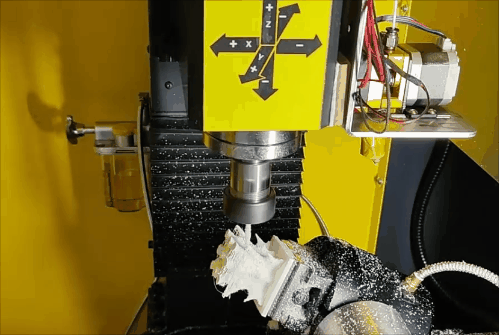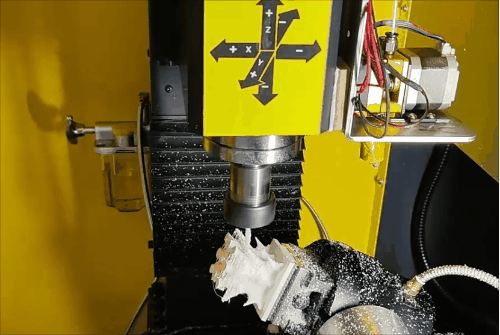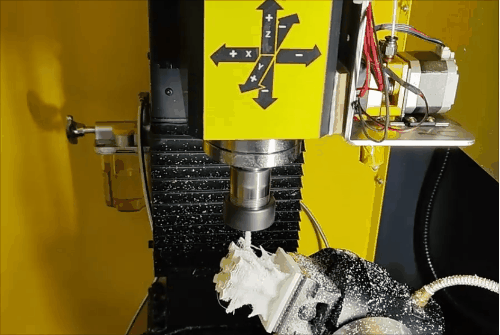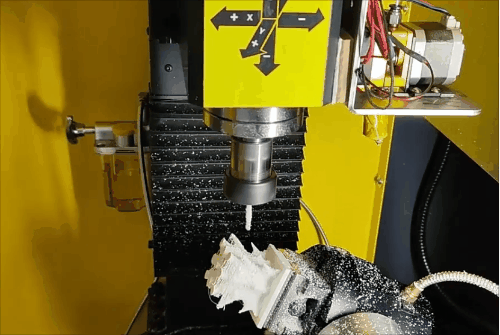
Stage 2 of hybrid fabrication.
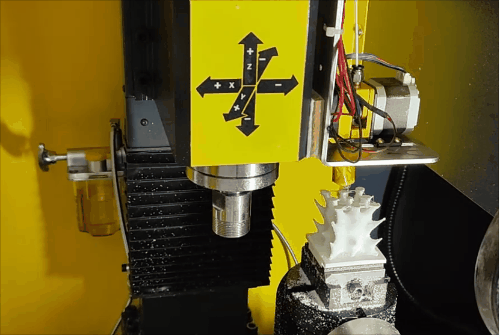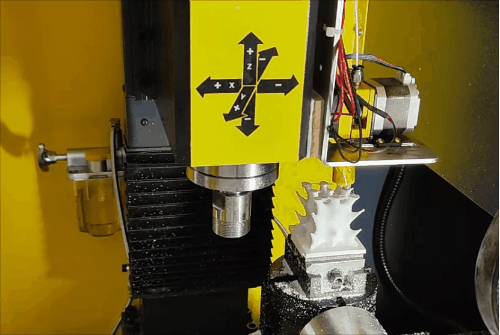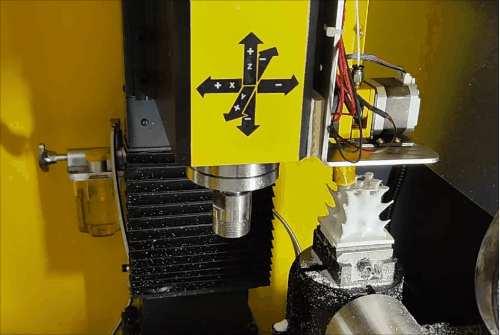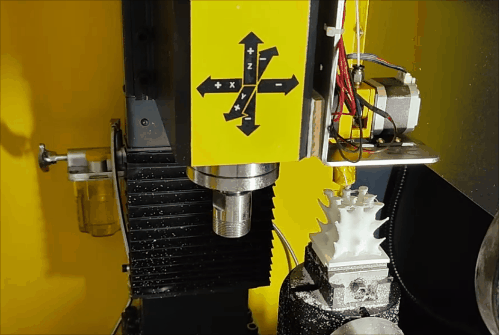
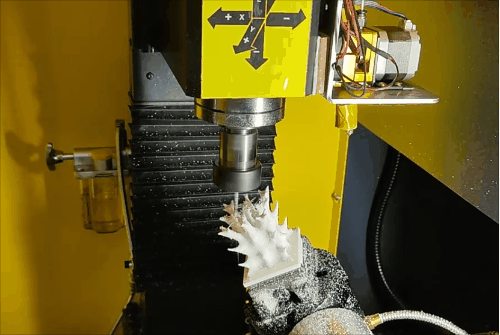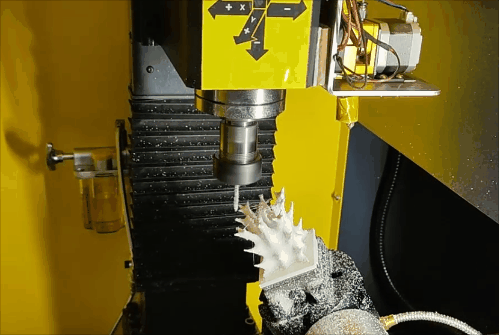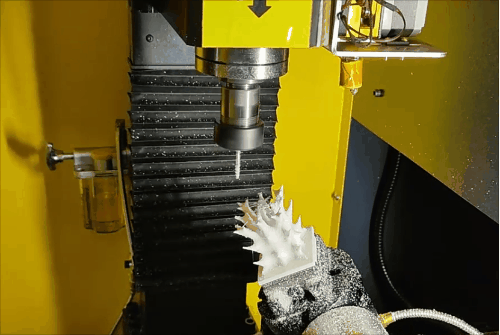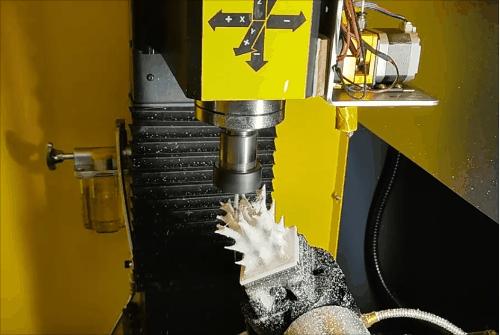
Stage 3 of hybrid fabrication.
Due to the CNC system limitations (open/close control of the extruder), retraction is not possible, leading to stringing and subpar surface quality during additive steps. However, this is fully corrected during subsequent subtractive machining, demonstrating the strength of HASM.
3.2.Final Prototype
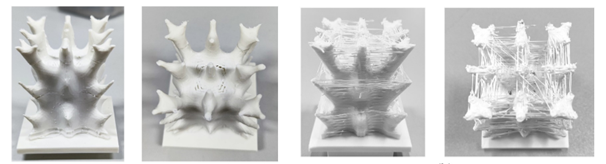
Successfully fabricated prototype without tool interference.
The fabricated prototype confirms that the topology-optimized structure is fully manufacturable with hybrid processes. Compared to pure additive manufacturing, the hybrid approach removes staircase effects and local material accumulations, resulting in visibly improved surface quality. Some minor interfacial gaps appear due to build direction transitions, an issue specific to extrusion-based AM and not present in laser-based metal AM.
Related Publication
[1] Xu, S., Liu, J., Yaji, K., & Lu, L. (2024). Topology optimization for hybrid additive-subtractive manufacturing incorporating dynamic process planning. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 431, 117270.
[2] Guo, Y., Xu, S., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Ahmad, R., & Ma, Y. (2025). DGTO: Derivable geodesics-coupled topology optimization for multi-axis hybrid additive and subtractive manufacturing with curved layer generation. Additive Manufacturing, 105, 104786.
[3] 徐庶之, 矢地謙太郎. (2025). Topology optimization for multi-axis additive subtractive manufacturing with curved layer generation. Proceedings of the Conference on Computational Engineering and Science / 日本計算工学会, Vol. 30, 113–118. 東京: 日本計算工学会.
